|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| ReadMe.md | ||
| __init__.py | ||
| master_qa.py | ||
ReadMe.md
Automation-Driven Manual QA
MasterQA uses SeleniumBase automation to speed up manual QA by having testers verify web pages after automation performs setup steps.
Here's the main code of basic_masterqa_test.py:
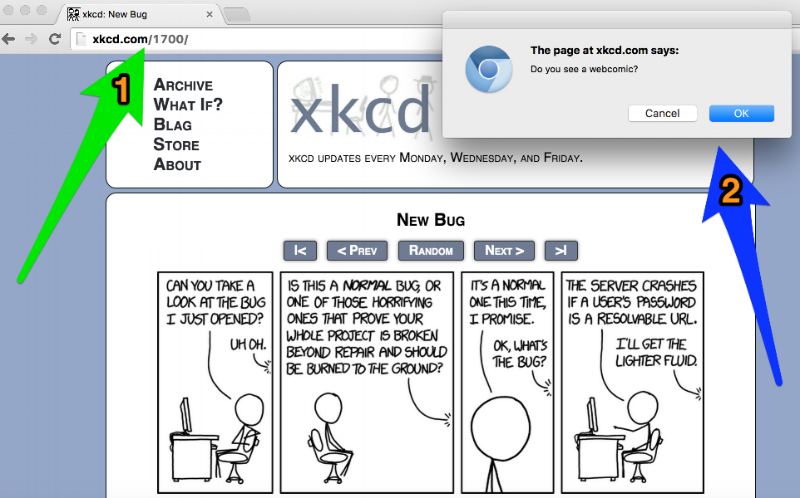
self.open("http://xkcd.com/1700/")
self.verify("Do you see a webcomic?")
self.click_link_text('Store')
self.verify("Do you see items for sale?")
self.update_text("input.search-input", "Robots\n")
self.verify("Do you see robots in the search results?")
After the web browser performs various automated actions, a pop-up window will ask the tester questions for each verification command. (See the screenshot below)
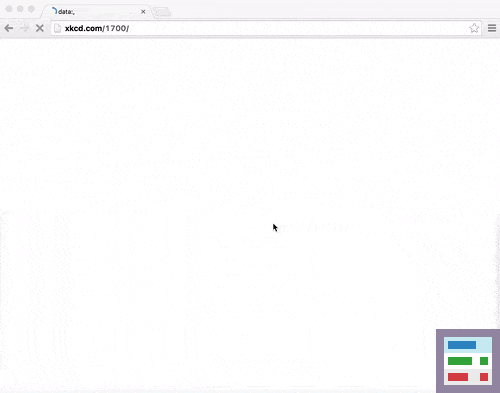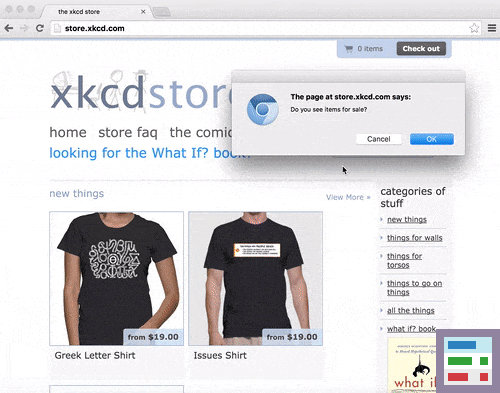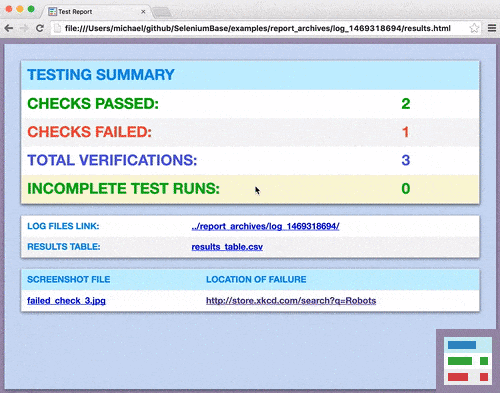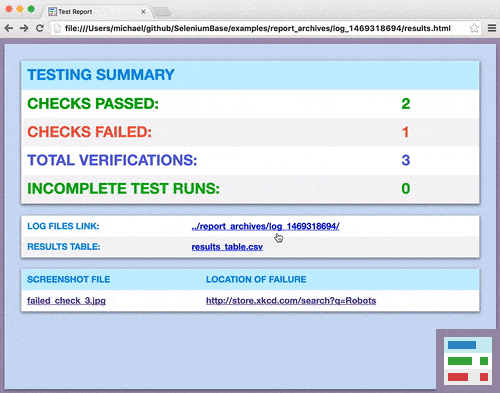
At the end of a full test run, as seen from this longer example, you'll see a results page that appears after responding to all the verification questions. (Failed verifications generate links to screenshots and log files.)
You may have noticed the Incomplete Test Runs row on the results page. If the value for that is not zero, it means that one of the automated steps failed. This could happen if you tell your script to perform an action on an element that doesn't exist. Now that we're mixing automation with manual QA, it's good to tell apart the failures from each. The results_table CSV file contains a spreadsheet with the details of each failure (if any) for both manual and automated steps.
How to run the example tests from scratch:
git clone https://github.com/seleniumbase/SeleniumBase.git
cd SeleniumBase
pip install -r requirements.txt
python setup.py install
cd examples
nosetests basic_masterqa_test.py --with-selenium
nosetests masterqa_test.py --with-selenium
At the end of your test run, you'll receive a report with results, screenshots, and log files. (Add --browser=chrome to your run command in order to use Chrome instead of Firefox, which requires Chromedriver installed.) Close the Results Page window when you're done.
Check out masterqa_test.py to learn how to write your own MasterQA tests:
You'll notice that tests are written based on SeleniumBase, with the key difference of using a different import: from seleniumbase import MasterQA rather than from seleniumbase import BaseCase. Now the test class will import MasterQA instead of BaseCase.
To add a manual verification step, use self.verify() in the code after each part of the script that needs manual verification. If you want to include a custom question, add text inside that call (in quotes). Example:
self.verify()
self.verify("Can you find the moon?")
MasterQA is powered by SeleniumBase, the most advanced open-source automation platform on the Planet.